Page 281 - ICSE Math 7
P. 281
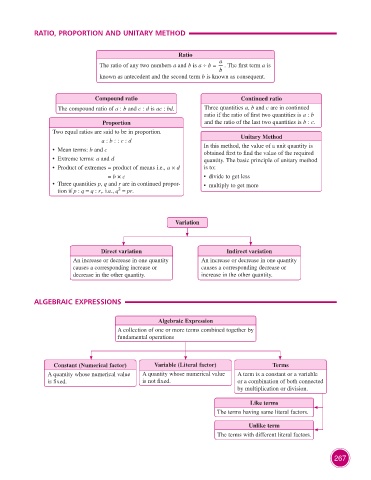
RATIO, PROPORTION AND UNITARY METHOD
Ratio
a
The ratio of any two numbers a and b is a ÷ b = . The first term a is
b
known as antecedent and the second term b is known as consequent.
Compound ratio Continued ratio
The compound ratio of a : b and c : d is ac : bd. Three quantities a, b and c are in continued
ratio if the ratio of first two quantities is a : b
Proportion and the ratio of the last two quantities is b : c.
Two equal ratios are said to be in proportion.
a : b : : c : d Unitary Method
• Mean terms: b and c In this method, the value of a unit quantity is
obtained first to find the value of the required
• Extreme terms: a and d quantity. The basic principle of unitary method
• Product of extremes = product of means i.e., a × d is to:
= b × c • divide to get less
• Three quantities p, q and r are in continued propor- • multiply to get more
2
tion if p : q = q : r,. i.e., q = pr.
Variation
Direct variation Indirect variation
An increase or decrease in one quantity An increase or decrease in one quantity
causes a corresponding increase or causes a corresponding decrease or
decrease in the other quantity. increase in the other quantity.
ALGEBRAIC EXPRESSIONS
Algebraic Expression
A collection of one or more terms combined together by
fundamental operations
Constant (Numerical factor) Variable (Literal factor) Terms
A quantity whose numerical value A quantity whose numerical value A term is a constant or a variable
is fixed. is not fixed. or a combination of both connected
by multiplication or division.
Like terms
The terms having same literal factors.
Unlike term
The terms with different literal factors.
267