Page 280 - ICSE Math 7
P. 280
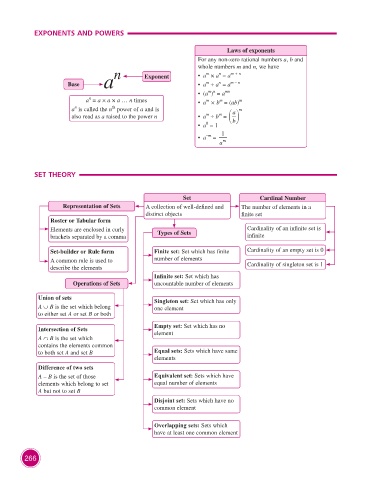
EXPONENTS AND POWERS
Laws of exponents
For any non-zero rational numbers a, b and
whole numbers m and n, we have
a n Exponent • a × a = a m + n
m
n
n
m
Base • a ÷ a = a m – n
m n
• (a ) = a mn
n
a = a × a × a … n times • a × b = (ab) m
m
m
n
th
a is called the n power of a and is m
a
m
m
also read as a raised to the power n • a ÷ b =
b
0
• a = 1
–m
• a = 1
a m
SET THEORY
Set Cardinal Number
Representation of Sets A collection of well-defined and The number of elements in a
distinct objects finite set
Roster or Tabular form
Elements are enclosed in curly Types of Sets Cardinality of an infinite set is
brackets separated by a comma infinite
Set-builder or Rule form Finite set: Set which has finite Cardinality of an empty set is 0
A common rule is used to number of elements
describe the elements Cardinality of singleton set is 1
Infinite set: Set which has
Operations of Sets uncountable number of elements
Union of sets Singleton set: Set which has only
A ∪ B is the set which belong one element
to either set A or set B or both
Intersection of Sets Empty set: Set which has no
element
A ∩ B is the set which
contains the elements common
to both set A and set B Equal sets: Sets which have same
elements
Difference of two sets
A – B is the set of those Equivalent set: Sets which have
elements which belong to set equal number of elements
A but not to set B
Disjoint set: Sets which have no
common element
Overlapping sets: Sets which
have at least one common element
266