Page 163 - ICSE Math 7
P. 163
15 Lines and Angles
Key Concepts
• Point, Line, Line Segment, Ray and Plane • Angle
• Parallel Lines, Intersecting Lines, Perpendicular Lines • Types of Angles
and Concurrent Lines
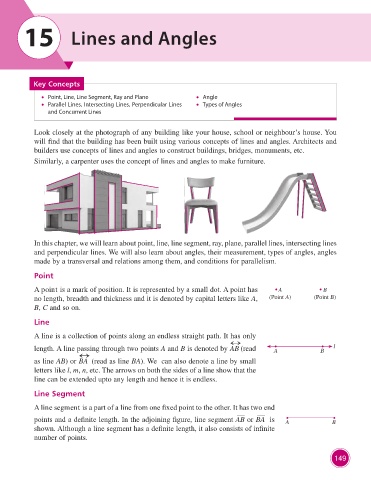
Look closely at the photograph of any building like your house, school or neighbour’s house. You
will find that the building has been built using various concepts of lines and angles. Architects and
builders use concepts of lines and angles to construct buildings, bridges, monuments, etc.
Similarly, a carpenter uses the concept of lines and angles to make furniture.
In this chapter, we will learn about point, line, line segment, ray, plane, parallel lines, intersecting lines
and perpendicular lines. We will also learn about angles, their measurement, types of angles, angles
made by a transversal and relations among them, and conditions for parallelism.
Point
A point is a mark of position. It is represented by a small dot. A point has A B
no length, breadth and thickness and it is denoted by capital letters like A, (Point A) (Point B)
B, C and so on.
Line
A line is a collection of points along an endless straight path. It has only
length. A line passing through two points A and B is denoted by AB (read A B l
as line AB) or BA (read as line BA). We can also denote a line by small
letters like l, m, n, etc. The arrows on both the sides of a line show that the
line can be extended upto any length and hence it is endless.
Line Segment
A line segment is a part of a line from one fixed point to the other. It has two end
points and a definite length. In the adjoining figure, line segment AB or BA is A B
shown. Although a line segment has a definite length, it also consists of infinite
number of points.
149