Page 38 - ICSE Math 6
P. 38
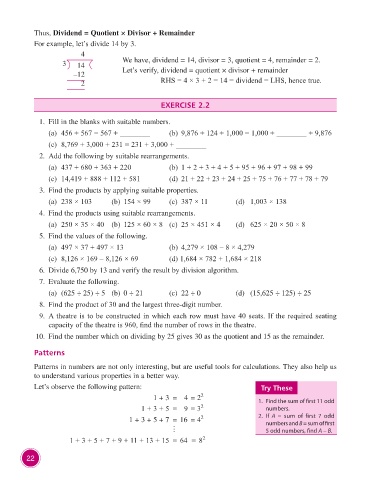
Thus, Dividend = Quotient × Divisor + Remainder
For example, let’s divide 14 by 3.
4
3 We have, dividend = 14, divisor = 3, quotient = 4, remainder = 2.
14
–12 Let’s verify, dividend = quotient × divisor + remainder
2 RHS = 4 × 3 + 2 = 14 = dividend = LHS, hence true.
EXERCISE 2.2
1. Fill in the blanks with suitable numbers.
(a) 456 + 567 = 567 + ________ (b) 9,876 + 124 + 1,000 = 1,000 + ________ + 9,876
(c) 8,769 + 3,000 + 231 = 231 + 3,000 + ________
2. Add the following by suitable rearrangements.
(a) 437 + 680 + 363 + 220 (b) 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5 + 95 + 96 + 97 + 98 + 99
(c) 14,419 + 888 + 112 + 581 (d) 21 + 22 + 23 + 24 + 25 + 75 + 76 + 77 + 78 + 79
3. Find the products by applying suitable properties.
(a) 238 × 103 (b) 154 × 99 (c) 387 × 11 (d) 1,003 × 138
4. Find the products using suitable rearrangements.
(a) 250 × 35 × 40 (b) 125 × 60 × 8 (c) 25 × 451 × 4 (d) 625 × 20 × 50 × 8
5. Find the values of the following.
(a) 497 × 37 + 497 × 13 (b) 4,279 × 108 – 8 × 4,279
(c) 8,126 × 169 – 8,126 × 69 (d) 1,684 × 782 + 1,684 × 218
6. Divide 6,750 by 13 and verify the result by division algorithm.
7. Evaluate the following.
(a) (625 ÷ 25) ÷ 5 (b) 0 ÷ 21 (c) 22 ÷ 0 (d) (15,625 ÷ 125) ÷ 25
8. Find the product of 30 and the largest three-digit number.
9. A theatre is to be constructed in which each row must have 40 seats. If the required seating
capacity of the theatre is 960, find the number of rows in the theatre.
10. Find the number which on dividing by 25 gives 30 as the quotient and 15 as the remainder.
Patterns
Patterns in numbers are not only interesting, but are useful tools for calculations. They also help us
to understand various properties in a better way.
Let’s observe the following pattern: Try These
1 + 3 = 4 = 2 2 1. Find the sum of first 11 odd
1 + 3 + 5 = 9 = 3 2 numbers.
1 + 3 + 5 + 7 = 16 = 4 2 2. If A = sum of first 7 odd
numbers and B = sum of first
5 odd numbers, find A – B.
1 + 3 + 5 + 7 + 9 + 11 + 13 + 15 = 64 = 8 2
22