Page 15 - Viva ICSE Computer Studies 4 : E-book
P. 15
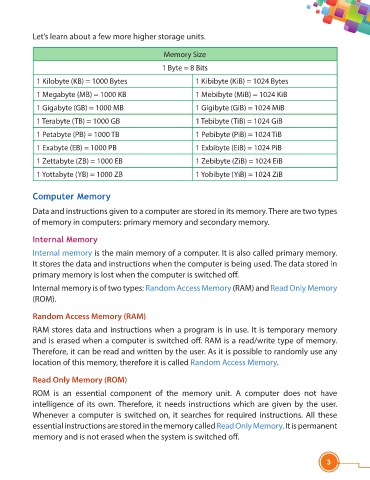
Let’s learn about a few more higher storage units.
Memory Size
1 Byte = 8 Bits
1 Kilobyte (KB) = 1000 Bytes 1 Kibibyte (KiB) = 1024 Bytes
1 Megabyte (MB) = 1000 KB 1 Mebibyte (MiB) = 1024 KiB
1 Gigabyte (GB) = 1000 MB 1 Gigibyte (GiB) = 1024 MiB
1 Terabyte (TB) = 1000 GB 1 Tebibyte (TiB) = 1024 GiB
1 Petabyte (PB) = 1000 TB 1 Pebibyte (PiB) = 1024 TiB
1 Exabyte (EB) = 1000 PB 1 Exbibyte (EiB) = 1024 PiB
1 Zettabyte (ZB) = 1000 EB 1 Zebibyte (ZiB) = 1024 EiB
1 Yottabyte (YB) = 1000 ZB 1 Yobibyte (YiB) = 1024 ZiB
Computer Memory
Data and instructions given to a computer are stored in its memory. There are two types
of memory in computers: primary memory and secondary memory.
Internal Memory
Internal memory is the main memory of a computer. It is also called primary memory.
It stores the data and instructions when the computer is being used. The data stored in
primary memory is lost when the computer is switched off .
Internal memory is of two types: Random Access Memory (RAM) and Read Only Memory
(ROM).
Random Access Memory (RAM)
RAM stores data and instructions when a program is in use. It is temporary memory
and is erased when a computer is switched off . RAM is a read/write type of memory.
Therefore, it can be read and written by the user. As it is possible to randomly use any
location of this memory, therefore it is called Random Access Memory.
Read Only Memory (ROM)
ROM is an essential component of the memory unit. A computer does not have
intelligence of its own. Therefore, it needs instructions which are given by the user.
Whenever a computer is switched on, it searches for required instructions. All these
essential instructions are stored in the memory called Read Only Memory. It is permanent
memory and is not erased when the system is switched off .
3