Page 49 - Viva ICSE Science 5 : E-book
P. 49
Corolla
The next whorl, corolla, consists of petals. All petals together are called corolla. They
are the most prominent part of a fl ower. They are usually brightly coloured and may
produce scents to attract insects.
Androecium
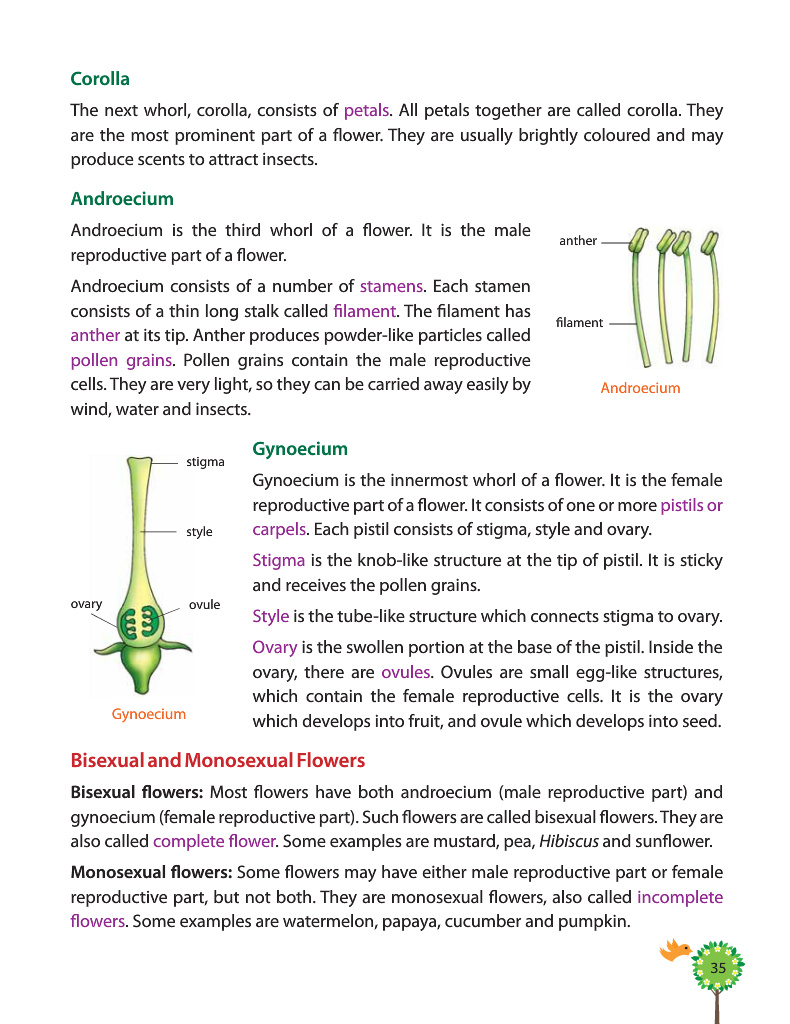
Androecium is the third whorl of a fl ower. It is the male
anther
reproductive part of a fl ower.
Androecium consists of a number of stamens. Each stamen
consists of a thin long stalk called fi lament. The fi lament has
fi lament
anther at its tip. Anther produces powder-like particles called
pollen grains. Pollen grains contain the male reproductive
cells. They are very light, so they can be carried away easily by Androecium
wind, water and insects.
Gynoecium
stigma
Gynoecium is the innermost whorl of a fl ower. It is the female
reproductive part of a fl ower. It consists of one or more pistils or
style carpels. Each pistil consists of stigma, style and ovary.
Stigma is the knob-like structure at the tip of pistil. It is sticky
and receives the pollen grains.
ovary ovule
Style is the tube-like structure which connects stigma to ovary.
Ovary is the swollen portion at the base of the pistil. Inside the
ovary, there are ovules. Ovules are small egg-like structures,
which contain the female reproductive cells. It is the ovary
Gynoecium
which develops into fruit, and ovule which develops into seed.
Bisexual and Monosexual Flowers
Bisexual fl owers: Most fl owers have both androecium (male reproductive part) and
gynoecium (female reproductive part). Such fl owers are called bisexual fl owers. They are
also called complete fl ower. Some examples are mustard, pea, Hibiscus and sunfl ower.
Monosexual fl owers: Some fl owers may have either male reproductive part or female
reproductive part, but not both. They are monosexual fl owers, also called incomplete
fl owers. Some examples are watermelon, papaya, cucumber and pumpkin.
35