Page 34 - Start Up Mathematics_7
P. 34
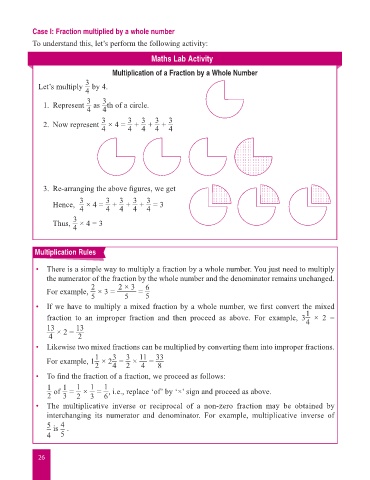
Case I: Fraction multiplied by a whole number
To understand this, let’s perform the following activity:
Maths Lab Activity
Multiplication of a Fraction by a Whole Number
3
Let’s multiply by 4.
4
3 3
1. Represent as th of a circle.
4 4
3 3 3 3 3
2. Now represent × 4 = + + +
4 4 4 4 4
3. Re-arranging the above figures, we get
3 3 3 3 3
Hence, × 4 = + + + = 3
4 4 4 4 4
3
Thus, × 4 = 3
4
Multiplication Rules
• There is a simple way to multiply a fraction by a whole number. You just need to multiply
the numerator of the fraction by the whole number and the denominator remains unchanged.
2
For example, × 3 = 2 × 3 = 6
5 5 5
• If we have to multiply a mixed fraction by a whole number, we first convert the mixed
1
fraction to an improper fraction and then proceed as above. For example, 3 × 2 =
4
13 × 2 = 13
4 2
• Likewise two mixed fractions can be multiplied by converting them into improper fractions.
1 3 3 11 33
For example, 1 × 2 = × =
2 4 2 4 8
• To find the fraction of a fraction, we proceed as follows:
1 1 1 1 1
of = × = , i.e., replace ‘of’ by ‘×’ sign and proceed as above.
2 3 2 3 6
• The multiplicative inverse or reciprocal of a non-zero fraction may be obtained by
interchanging its numerator and denominator. For example, multiplicative inverse of
4
5 is .
4 5
26