Page 165 - Start Up Mathematics_7
P. 165
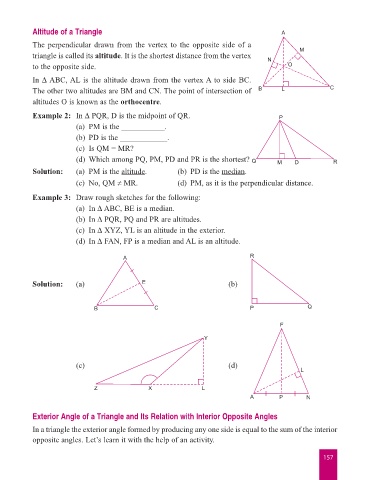
Altitude of a Triangle A
The perpendicular drawn from the vertex to the opposite side of a M
triangle is called its altitude. It is the shortest distance from the vertex N
to the opposite side. O
In ∆ ABC, AL is the altitude drawn from the vertex A to side BC.
The other two altitudes are BM and CN. The point of intersection of B L C
altitudes O is known as the orthocentre.
Example 2: In ∆ PQR, D is the midpoint of QR. P
(a) PM is the ___________.
(b) PD is the ____________.
(c) Is QM = MR?
(d) Which among PQ, PM, PD and PR is the shortest? Q M D R
Solution: (a) PM is the altitude. (b) PD is the median.
(c) No, QM ≠ MR. (d) PM, as it is the perpendicular distance.
Example 3: Draw rough sketches for the following:
(a) In ∆ ABC, BE is a median.
(b) In ∆ PQR, PQ and PR are altitudes.
(c) In ∆ XYZ, YL is an altitude in the exterior.
(d) In ∆ FAN, FP is a median and AL is an altitude.
A R
Solution: (a) E (b)
B C P Q
F
Y
(c) (d)
L
Z X L
A P N
Exterior Angle of a Triangle and Its Relation with Interior Opposite Angles
In a triangle the exterior angle formed by producing any one side is equal to the sum of the interior
opposite angles. Let’s learn it with the help of an activity.
157