Page 260 - Start Up Mathematics_6
P. 260
14 Practical Geometry
Everything we see around us has a shape. Even the book you are reading has a shape. We have
already learnt about some simple shapes and how to draw them. In this chapter, we will learn
about some basic constructions like drawing circles, line segments, perpendiculars, perpendicular-
bisectors and some special angles. For these we will use various instruments like ruler, compass,
protractor, divider and set square present in the geometry box. We have already learnt how to use
ruler, divider and protractor in earlier chapters. We shall learn about use of the rest of them in this
chapter.
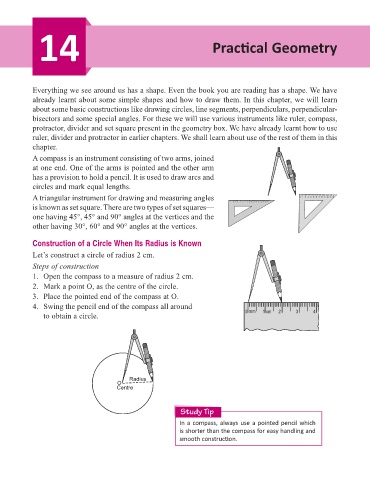
A compass is an instrument consisting of two arms, joined
at one end. One of the arms is pointed and the other arm
has a provision to hold a pencil. It is used to draw arcs and
circles and mark equal lengths.
A triangular instrument for drawing and measuring angles
is known as set square. There are two types of set squares—
one having 45°, 45° and 90° angles at the vertices and the
other having 30°, 60° and 90° angles at the vertices.
Construction of a Circle When Its Radius is Known
Let’s construct a circle of radius 2 cm.
Steps of construction
1. Open the compass to a measure of radius 2 cm.
2. Mark a point O, as the centre of the circle.
3. Place the pointed end of the compass at O.
4. Swing the pencil end of the compass all around
to obtain a circle.
Radius
O
Centre
Study Tip
In a compass, always use a pointed pencil which
is shorter than the compass for easy handling and
smooth construction.