Page 232 - ICSE Math 8
P. 232
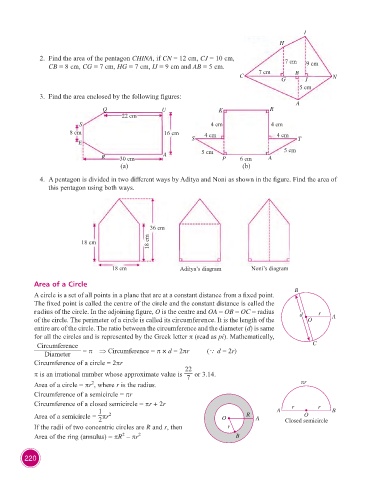
I
H
2. Find the area of the pentagon CHINA, if CN = 12 cm, CJ = 10 cm, 7 cm
CB = 8 cm, CG = 7 cm, HG = 7 cm, IJ = 9 cm and AB = 5 cm. 9 cm
C 7 cm B N
G J
5 cm
3. Find the area enclosed by the following figures:
A
Q U K R
22 cm
S 4 cm 4 cm
8 cm 16 cm 4 cm 4 cm
E S T
R 30 cm A 5 cm P 6 cm A 5 cm
(a) (b)
4. A pentagon is divided in two different ways by Aditya and Noni as shown in the figure. Find the area of
this pentagon using both ways.
36 cm
18 cm
18 cm
18 cm Aditya’s diagram Noni’s diagram
Area of a Circle
B
A circle is a set of all points in a plane that are at a constant distance from a fixed point.
The fixed point is called the centre of the circle and the constant distance is called the
radius of the circle. In the adjoining figure, O is the centre and OA = OB = OC = radius d r
of the circle. The perimeter of a circle is called its circumference. It is the length of the O A
entire arc of the circle. The ratio between the circumference and the diameter (d) is same
for all the circles and is represented by the Greek letter π (read as pi). Mathematically,
Circumference C
Diameter = π ⇒ Circumference = π × d = 2πr ( d = 2r)
Circumference of a circle = 2πr
22
π is an irrational number whose approximate value is 7 or 3.14.
2
Area of a circle = πr , where r is the radius. πr
Circumference of a semicircle = πr
Circumference of a closed semicircle = πr + 2r r r
1 A B
O
Area of a semicircle = πr 2 O R A Closed semicircle
2
If the radii of two concentric circles are R and r, then r
2
Area of the ring (annulus) = πR – πr 2 B
220