Page 58 - ICSE Math 7
P. 58
1
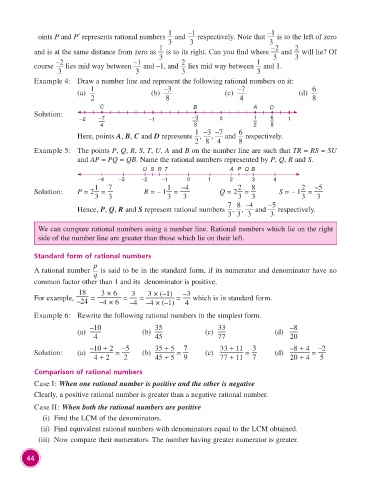
Points P and P′ represents rational numbers and –1 respectively. Note that –1 is to the left of zero
3
3
3
2
1
and is at the same distance from zero as is to its right. Can you find where –2 and will lie? Of
–2 –1 3 2 1 3 3
course lies mid way between and –1, and lies mid way between and 1.
3 3 3 3
Example 4: Draw a number line and represent the following rational numbers on it:
(a) 1 (b) –3 (c) –7 (d) 6
2 8 4 8
C B A D
Solution:
–2 –7 –1 –3 0 1 6 1
4 8 2 8
6
1 –3 –7
Here, points A, B, C and D represents , , and respectively.
2 8 4 8
Example 5: The points P, Q, R, S, T, U, A and B on the number line are such that TR = RS = SU
and AP = PQ = QB. Name the rational numbers represented by P, Q, R and S.
U S R T A P Q B
–4 –3 –2 –1 0 1 2 3 4
1
2
1
7
8
2
Solution: P = 2 = R = – 1 = –4 Q = 2 = S = – 1 = –5
3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3
7 8 –4 –5
Hence, P, Q, R and S represent rational numbers , , and respectively.
3 3 3 3
We can compare rational numbers using a number line. Rational numbers which lie on the right
side of the number line are greater than those which lie on their left.
Standard form of rational numbers
p
A rational number is said to be in the standard form, if its numerator and denominator have no
q
common factor other than 1 and its denominator is positive.
18 3 × 6 3 3 × (–1) –3
For example, –24 = –4 × 6 = –4 = –4 × (–1) = 4 which is in standard form.
Example 6: Rewrite the following rational numbers in the simplest form.
–10 35 33 –8
(a) (b) (c) (d)
4 45 77 20
–10 ÷ 2 –5 35 ÷ 5 7 33 ÷ 11 3 –8 ÷ 4 –2
Solution: (a) = (b) = (c) = (d) =
4 ÷ 2 2 45 ÷ 5 9 77 ÷ 11 7 20 ÷ 4 5
Comparison of rational numbers
Case I: When one rational number is positive and the other is negative
Clearly, a positive rational number is greater than a negative rational number.
Case II: When both the rational numbers are positive
(i) Find the LCM of the denominators.
(ii) Find equivalent rational numbers with denominators equal to the LCM obtained.
(iii) Now compare their numerators. The number having greater numerator is greater.
44