Page 57 - ICSE Math 7
P. 57
Example 1: Write the next four rational numbers in each of the
following patterns. Maths Info
–2 –4 –6 –1 –2 –3 Iff implies if and only if, i.e.,
(a) , , , … (b) , , , … either both the statement are
7 14 21 5 10 15 true or both are false.
,
,
,
,
,
Solution: (a) –8 –10 –12 –14 (b) –4 –5 –6 –7 a iff b ⇒ a ⇔ b
,
28 35 42 49 20 25 30 35 (i) If a is true, then b is true.
(ii) If b is true, then a is true.
Example 2: Give four rational numbers equivalent to:
–3 2
(a) (b)
4 9
,
,
,
Solution: (a) –6 –9 –12 –15 (b) 4 , 6 , 8 10
,
8 12 16 20 18 27 36 45
Example 3: Which of the following pairs represent the same rational number?
(a) 2 and –5 (b) –1 and 1
8 20 –3 3
1
1
1
Solution: (a) 2 = and –5 = –1 (b) –1 = and = 1
8 4 20 4 –3 3 3 3
1 –1 1 1
≠ =
4 4 3 3
∴ given rational numbers are different. ∴ given rational numbers are the same.
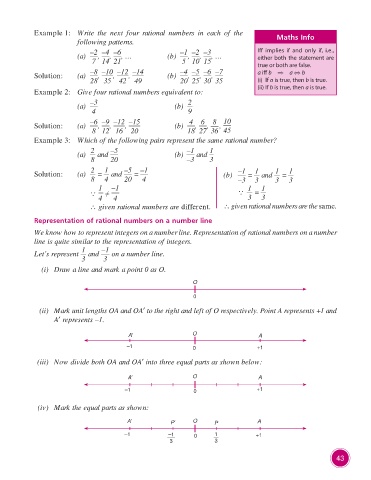
Representation of rational numbers on a number line
We know how to represent integers on a number line. Representation of rational numbers on a number
line is quite similar to the representation of integers.
1
Let’s represent and –1 on a number line.
3 3
(i) Draw a line and mark a point 0 as O.
O
0
(ii) Mark unit lengths OA and OA′ to the right and left of O respectively. Point A represents +1 and
A′ represents –1.
A′ O A
–1 0 +1
(iii) Now divide both OA and OA′ into three equal parts as shown below:
A′ O A
–1 0 +1
(iv) Mark the equal parts as shown:
A′ P′ O P A
–1 –1 0 1 +1
3 3
43