Page 191 - ICSE Math 7
P. 191
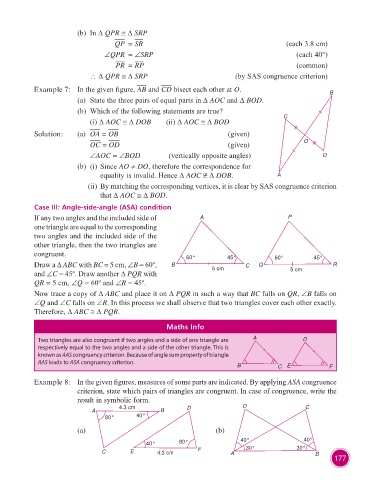
(b) In ∆ QPR ∆ SRP
QP = SR (each 3.8 cm)
∠QPR = ∠SRP (each 40°)
PR = RP (common)
∴ ∆ QPR ∆ SRP (by SAS congruence criterion)
Example 7: In the given figure, AB and CD bisect each other at O.
B
(a) State the three pairs of equal parts in ∆ AOC and ∆ BOD.
(b) Which of the following statements are true?
C
(i) ∆ AOC ∆ DOB (ii) ∆ AOC ∆ BOD
Solution: (a) OA = OB (given)
OC = OD (given) O
∠AOC = ∠BOD (vertically opposite angles) D
(b) (i) Since AO ≠ DO, therefore the correspondence for
equality is invalid. Hence ∆ AOC ∆ DOB. A
(ii) By matching the corresponding vertices, it is clear by SAS congruence criterion
that ∆ AOC ∆ BOD.
Case III: Angle-side-angle (ASA) condition
If any two angles and the included side of A P
one triangle are equal to the corresponding
two angles and the included side of the
other triangle, then the two triangles are
congruent. 60° 45° 60° 45°
Draw a ∆ ABC with BC = 5 cm, ∠B = 60º, B 5 cm C Q R
and ∠C = 45º. Draw another ∆ PQR with 5 cm
QR = 5 cm, ∠Q = 60º and ∠R = 45º.
Now trace a copy of ∆ ABC and place it on ∆ PQR in such a way that BC falls on QR, ∠B falls on
∠Q and ∠C falls on ∠R. In this process we shall observe that two triangles cover each other exactly.
Therefore, ∆ ABC ∆ PQR.
Maths Info
Two triangles are also congruent if two angles and a side of one triangle are A D
respectively equal to the two angles and a side of the other triangle. This is
known as AAS congruency criterion. Because of angle sum property of triangle
AAS leads to ASA congruency criterion.
B C E F
Example 8: In the given figures, measures of some parts are indicated. By applying ASA congruence
criterion, state which pairs of triangles are congruent. In case of congruence, write the
result in symbolic form.
4.3 cm D D C
A B
80° 40°
(a) (b)
40° 80° 40° 40°
C E 4.3 cm F A 30° 30° B
177