Page 263 - Start Up Mathematics_7
P. 263
15 Visualizing Solid Shapes
In our day-to-day life, we see several objects around us. On careful observation, we find they
may have different shapes and sizes, but yet they may have a common feature in terms of their
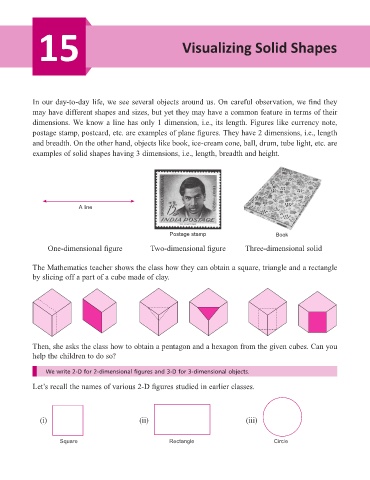
dimensions. We know a line has only 1 dimension, i.e., its length. Figures like currency note,
postage stamp, postcard, etc. are examples of plane figures. They have 2 dimensions, i.e., length
and breadth. On the other hand, objects like book, ice-cream cone, ball, drum, tube light, etc. are
examples of solid shapes having 3 dimensions, i.e., length, breadth and height.
A line
Postage stamp Book
One-dimensional figure Two-dimensional figure Three-dimensional solid
The Mathematics teacher shows the class how they can obtain a square, triangle and a rectangle
by slicing off a part of a cube made of clay.
Then, she asks the class how to obtain a pentagon and a hexagon from the given cubes. Can you
help the children to do so?
We write 2-D for 2-dimensional figures and 3-D for 3-dimensional objects.
Let’s recall the names of various 2-D figures studied in earlier classes.
(i) (ii) (iii)
Square Rectangle Circle