Page 202 - Start Up Mathematics_6
P. 202
Solution:
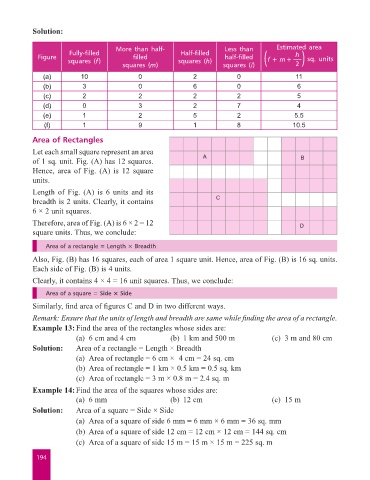
More than half- Less than Estimated area
Fully-filled Half-filled h
Figure filled half-filled sq. units
squares (f) squares (h) f + m +
squares (m) squares (l) 2
(a) 10 0 2 0 11
(b) 3 0 6 0 6
(c) 2 2 2 2 5
(d) 0 3 2 7 4
(e) 1 2 5 2 5.5
(f) 1 9 1 8 10.5
Area of Rectangles
Let each small square represent an area
of 1 sq. unit. Fig. (A) has 12 squares. A B
Hence, area of Fig. (A) is 12 square
units.
Length of Fig. (A) is 6 units and its
breadth is 2 units. Clearly, it contains C
6 × 2 unit squares.
Therefore, area of Fig. (A) is 6 × 2 = 12 D
square units. Thus, we conclude:
Area of a rectangle = Length × Breadth
Also, Fig. (B) has 16 squares, each of area 1 square unit. Hence, area of Fig. (B) is 16 sq. units.
Each side of Fig. (B) is 4 units.
Clearly, it contains 4 × 4 = 16 unit squares. Thus, we conclude:
Area of a square = Side × Side
Similarly, find area of figures C and D in two different ways.
Remark: Ensure that the units of length and breadth are same while finding the area of a rectangle.
Example 13: Find the area of the rectangles whose sides are:
(a) 6 cm and 4 cm (b) 1 km and 500 m (c) 3 m and 80 cm
Solution: Area of a rectangle = Length × Breadth
(a) Area of rectangle = 6 cm × 4 cm = 24 sq. cm
(b) Area of rectangle = 1 km × 0.5 km = 0.5 sq. km
(c) Area of rectangle = 3 m × 0.8 m = 2.4 sq. m
Example 14: Find the area of the squares whose sides are:
(a) 6 mm (b) 12 cm (c) 15 m
Solution: Area of a square = Side × Side
(a) Area of a square of side 6 mm = 6 mm × 6 mm = 36 sq. mm
(b) Area of a square of side 12 cm = 12 cm × 12 cm = 144 sq. cm
(c) Area of a square of side 15 m = 15 m × 15 m = 225 sq. m
194