Page 172 - Start Up Mathematics_4
P. 172
• The measure of the long side is called the length of the rectangle.
• The measure of the short side is called the breadth or width of the rectangle.
• The two long sides AB and DC are opposite to each other and are equal (AB = DC).
• The two short sides AD and BC are opposite to each other and are equal (AD = BC).
• It has four vertices A, B, C and D.
Square: A square is a rectangle that has all four sides equal.
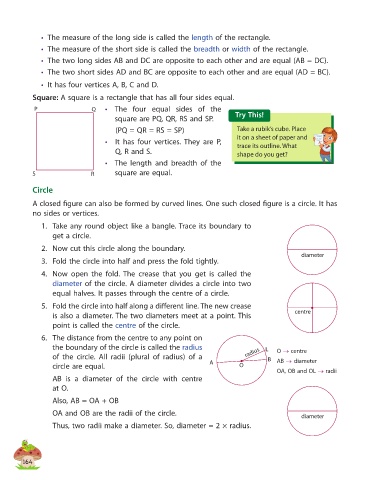
P Q • The four equal sides of the
square are PQ, QR, RS and SP. Try This!
(PQ = QR = RS = SP) Take a rubik’s cube. Place
it on a sheet of paper and
• It has four vertices. They are P, trace its outline. What
Q, R and S. shape do you get?
• The length and breadth of the
S R square are equal.
Circle
A closed figure can also be formed by curved lines. One such closed figure is a circle. It has
no sides or vertices.
1. Take any round object like a bangle. Trace its boundary to
get a circle.
2. Now cut this circle along the boundary.
diameter
3. Fold the circle into half and press the fold tightly.
4. Now open the fold. The crease that you get is called the
diameter of the circle. A diameter divides a circle into two
equal halves. It passes through the centre of a circle.
5. Fold the circle into half along a different line. The new crease
is also a diameter. The two diameters meet at a point. This centre
point is called the centre of the circle.
6. The distance from the centre to any point on
the boundary of the circle is called the radius L O → centre
of the circle. All radii (plural of radius) of a radius B AB → diameter
circle are equal. A O
OA, OB and OL → radii
AB is a diameter of the circle with centre
at O.
Also, AB = OA + OB
OA and OB are the radii of the circle. diameter
Thus, two radii make a diameter. So, diameter = 2 × radius.
164